Refrigeration solutions for the agri-food industry
INTARCON2024-12-12T07:58:53+01:00We all know the socio-economic and environmental benefits that are achieved by increasing the shelf life of foodstuffs. We attribute this to the constant improvements and innovations in the refrigeration sector for the agri-food industry. But how is this possible?
As reflected by the WHO (World Health Organisation), in one of its five keys to maintaining food safety (“Key 4: Keep food at safe temperatures: At temperatures below 5°C microbial growth slows or stops”), refrigeration is one of the great allies in food preservation. This is why advances in the field of refrigeration for the agri-food industry are constantly being made in order to provide solutions by increasing energy efficiency and reducing the ecological footprint. Ultimately, achieving the most important goal for our society, optimising agri-food production.
New paradigms in preservation and refrigeration for the agri-food industry
- The development of energy-efficient air conditioning and refrigeration equipment that complies with strict environmental regulations, such as the ErP 2015/1095/EU directive on Ecodesign requirements, which requires minimum COP (Coefficient of Performance) and SEPR (Seasonal Performance Factor) values.
- The use of cold rooms and freezing tunnels.
- The evolution of heat recovery systems, which improve the efficiency of the system as a whole (e.g. dairy industry, milk cooling – heat for pasteurisation).
- The substitution of materials, such as steel for aluminium, and the use of materials with reduced environmental impact composed of natural fibres; reducing the weight, cost and ecological footprint of the equipment.
- The emergence of regulation and control via IoT (Internet Of Things), based on the creation of a network of devices and the technology that facilitates communication between them and the cloud. This makes it possible to optimise the operation of the installation thanks to the capacity for continuous improvement through the collection and processing of data.
Innovative preservation techniques under development for refrigeration in the agri-food industry
- Lyophilisation. Dehydro-freezing or cryodrying process in vacuum rooms coupled to refrigeration systems.
- Modified atmosphere rooms (they use nitrogen generators, CO2 absorbers or ethylene scrubbers that allow the control of the atmosphere in which the fruit and vegetable product is conserved, in order to reduce respiration and slow down ripening).
- High hydrostatic pressure rooms (sterilise while maintaining the organoleptic and nutritional properties of the food, unlike heat application techniques).
- Sterilisation with supercritical CO2. CO2 has a low critical temperature of 31°C, so that thermosensitive organic compounds can be processed without danger of denaturation or decomposition, and it is an inexpensive and non-toxic refrigerant.
- Ultrasound-assisted freezing (using ultrasound to reduce the size of ice crystals formed during the freezing process).
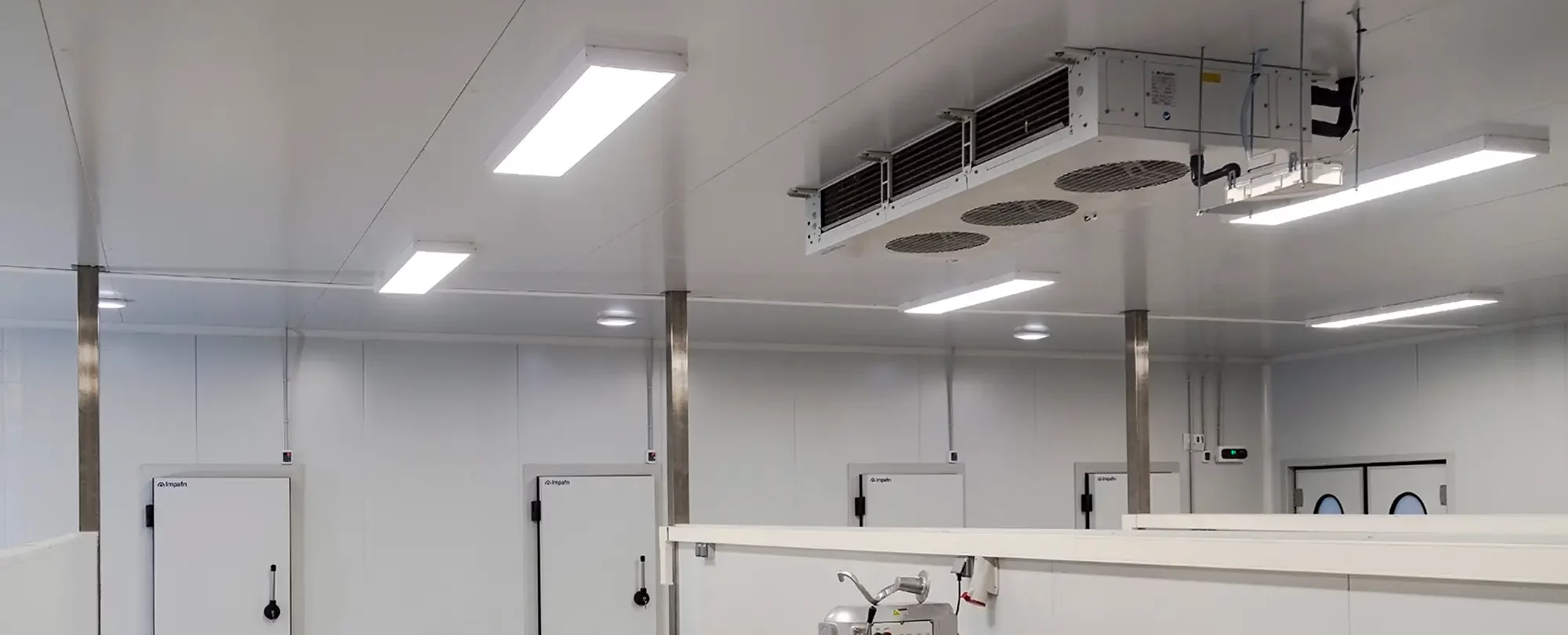

INTARCON's development and commitment to the importance of refrigeration for the agri-food industry
Some of these techniques are developed and researched by INTARCON. Direct contact with our clients allows us to understand the problems they face and to solve their main concerns:
- The risk of product loss due to leakage.
- Equipment failure due to defective compressor.
- Malfunctioning at extreme temperatures.
- High electricity consumption.
- Refrigerant gas costs.
- Etc.
Day after day we work on the improvement of the equipment in order to give the best product and service, providing: precision, reliability and efficiency to the installation.
INTARCON works to avoid the interruption of the cold chain (visible in the formation of frost or dense blocks), in order to achieve an increase in the shelf life and food safety, and stability in the process line under food safety standards and maintenance of the organoleptic properties of the product.
INTARCON's refrigeration technologies for the agri-food industry
Natural refrigerants
CO2 plants
High-powered equipment with double suction, providing service at medium and very low temperature (deep-freezing) simultaneously.
Indirect systems
Water glycol refrigeration systems (Waterloop system, chiller, glycol ring and air coolers) reduce the refrigerant charge in the system to a minimum. This eliminates the risk of possible HFC leaks and high refrigerant line charging costs. In addition to maintaining a production line and atmosphere free of contaminants, minimising the risk of product spoilage and potential risks to personnel and stored product.
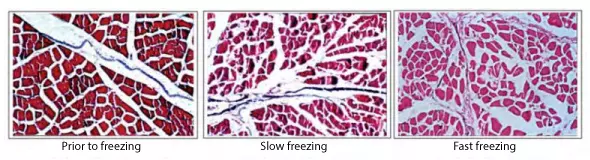
Abatement evaporators for freezing tunnels
They serve one of the most important stages in food preservation, in order to avoid the typical problems of freezing due to the formation of ice crystals in the intercellular spaces. This causes water to escape from the cells to compensate for the increase in osmotic pressure, which causes the product to dry out and thus weight loss. For this purpose, equipment has been designed with high-flow, high static pressure fans and high-efficiency coils to reduce freezing time and encourage the formation of smaller crystals, thus reducing the loss of organoleptic and physicochemical properties.
Air sanitisation and HEPA filter sterilisation systems
This is the case of our intarSANIT, which works by ultraviolet-C (UV-C) light treatment in food processing rooms and areas with requirements for strict control of bioaerosols and suspended particulate matter (bacteria, fungi, viruses, PM2.5, etc.).
Battery dimensions for tropicalised environment (45ºC and 50ºC)
Increasing maximum temperatures and export to tropical areas have led to a battery design with an operating range adapted to this new situation.
Equipment with specific design and functions such as:
- Wine cellar refrigeration systems.
- Meat preservation and maturation systems.
Design of systems with independent cooling circuits
It allows the system to continue to operate at a lower cooling capacity in the event of a fault while the faulty circuit is being serviced or repaired.
Equipment with design and functions for increased energy efficiency
- Capacity variation system (CRV). A set of valves that allows the cooling capacity of a compressor to be progressively varied while reducing the electrical power absorbed and protecting the compressor. This system results in uniform chamber temperatures with fewer compressor stops/starts, allowing suction line pressure to be kept constant.
- Vapour injection system. Based on the use of an exchanger that causes the liquid to subcool at the condenser outlet and the refrigerant to evaporate in the suction line. In this way, it injects vapour halfway through the compression cycle and reduces the gas discharge temperature. Finally, it increases the cooling capacity and efficiency of the refrigerant circuit.
- Free Cooling. Suitable for environments where the outside temperature is sufficiently low during the winter months. In this way, it allows the exchange of water or glycol temperature with the environment to dispense with compression and its electrical consumption.
Energy-efficient equipment
- Heat recovery systems. They allow the heat energy to be dissipated in the condenser to be reused by the system, giving rise to domestic hot water (DHW), necessary for the sanitisation of surfaces. Avoiding the use of combustion systems such as boilers or electrical systems to obtain it (e.g. brewery, dairy industry…).
- Floating condensation. In air-condensing equipment, it generates significant energy savings by allowing the speed of the fans to be modulated according to the variation in outside temperature.
- Hot gas defrosting. It allows using the high discharge temperature of the compressor to defrost the frost formed in the evaporator of the chamber, avoiding the heat supply by means of electrical resistances and thus reducing electricity consumption.
- Intelligent defrosting. It consists of carrying out the necessary defrosts and discarding the programmed ones, thanks to previous records of their duration or the time of frost formation.
- Frequency inverters (Inverter). They are applied to compressors, fans and hydraulic pumps, with the aim of reducing electricity consumption by making electronic soft starts and modulating the rotational speed of the motors, extending the useful life of these components.
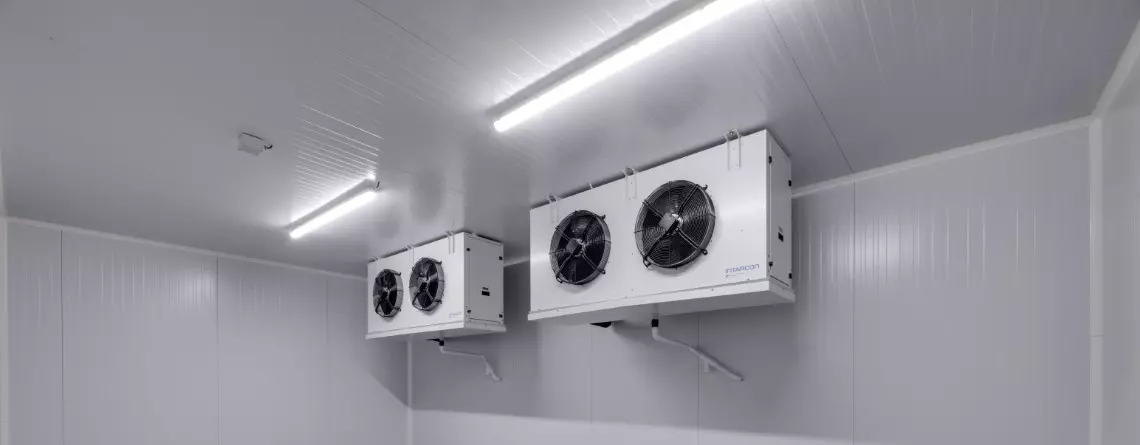

Optional
Some of the most significant optionals in refrigeration solutions for the agri-food industry are also worth mentioning:
- Anti-corrosion treatment of batteries. It is a polyurethane coating that prevents corrosion of the battery when exposed to saline and high humidity environments (e.g.: condensers in coastal areas, evaporators in fish or seafood chambers, etc.).
- Warm-up sleeves. They prevent heat transmission to the chamber during evaporator defrosting. In order to minimise temperature fluctuations inside the chamber and avoid disruption of the cold chain.
- Digitalisation system (Kiconex). Advances in equipment monitoring are enabling a major transformation of the sector, leading to advances in:
- Automation and data collection.
- Reduction of time during preventive maintenance.
- Ability to foresee and visualise possible equipment failures remotely.
- Exhaustive control of the equipment allowing remote adjustment of equipment operation.
In the future, social demands will increase in terms of food safety, efficient energy consumption, use of sustainable materials and equipment, etc.
In the meantime, INTARCON continues to work on solving future requirements.