The importance of refrigeration in food
INTARCON2022-07-12T14:13:55+02:00Most of the foodstuffs consumed daily nowadays need to be refrigerated because they are perishable (meat, fish, fruit, vegetables, etc.). For this reason, it is essential to guarantee their safety for as long as possible, thus avoiding possible health problems.
What is the importance of refrigerating food?
It has been proven that refrigeration of food at an optimum temperature plays a fundamental role in maintaining food safety. In many cases it is necessary to control and maintain the storage temperature, which will be different for each type of product.
In addition, if we lower the storage temperature of perishable foods, we will be able to significantly reduce the reproduction speed of the vast majority of microorganisms. These are the cause of decomposition, favouring the loss of product quality and generating possible illnesses in consumers.
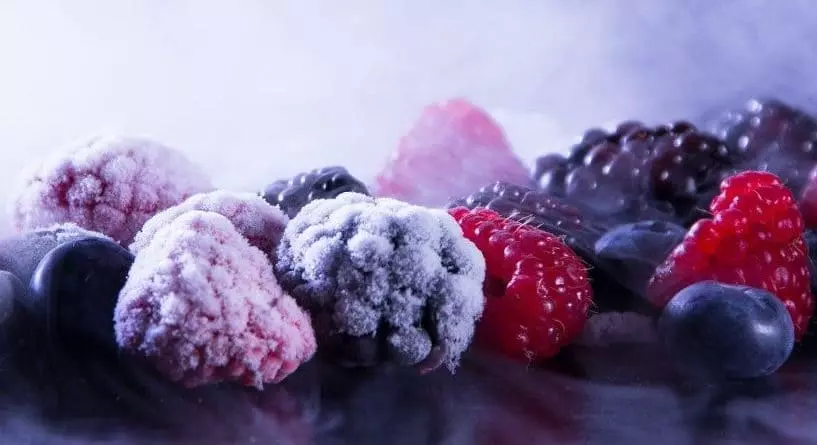
Refrigeration slows down the metabolism of organic matter to a near standstill at -18°C (the international standard for most frozen products). At this temperature, the partial or total inhibition of altering processes in food, such as certain enzymatic reactions or the metabolic degradation of proteins, is achieved. This slows down the decomposition and spoilage of these foods, as well as preventing possible health problems after consumption.
Food preservation processes.
Over the years, a number of processes have been known to achieve food preservation, using different methods. These processes try to slow down the growth of micro-organisms and therefore the properties of the food, although this is not always possible. The two most common ways of preserving food today are:
- Refrigeration: This consists of keeping food at a temperature, between 0 °C and 8 °C, close to freezing point. It is usually used for fresh food to slow down microbial growth.
- Freezing: This involves lowering the temperature of the food to below freezing point, usually between -18 °C and -35 °C. Depending on the type of product, thus making bacterial growth impossible.

Other food preservation processes
In addition, there are other types of preservation processes which, although with different qualities, also aim to preserve the optimum conditions for food consumption, among which the following stand out:
- Ultra-freezing: consists of subjecting food to temperatures below -40ºC for relatively short periods of time (< 120 min).
- Boiling: process prior to freezing in some cases, which involves boiling the food before freezing.
- Sterilisation: this is one of the safest methods of food preservation, although subjecting food to high temperatures alters its properties.
- Pasteurisation: this is similar to sterilisation, although lower temperatures are applied and therefore it is less effective. In order to be preserved correctly, it would have to be refrigerated afterwards or the microorganisms would recover their activity, although more slowly, for example, milk after being opened from the container.
- Fermentation: this is a preservation process based on the generation of microorganisms that are not harmful to health, but which significantly alter the properties of the product. In most cases, this alteration is provoked in order to obtain a final product such as wine or cheese.
- Desiccation: process that consists of making the food lose its moisture in a natural way, so that the microorganisms do not have liquid water.
- Smoking: a preservation process that consists of exposing a food to smoke, altering its properties.
- Vacuum packaging: consists of extracting the air that surrounds the food and in this way there is no incidence of air or microorganisms, although some of its properties, such as its shape, may be altered.
- Addition of salt or salting: this is one of the oldest preservation methods in history and involves adding salt to food.
- Preservation by chemical means: this involves the addition of chemical substances that nullify the activity of micro-organisms in the food, although in large quantities, they can alter its optimum conditions…
- Sugar concentrates: this consists of adding sugars to natural foods, mainly fruit, with the intention of preventing oxidation of the fruit and thus avoiding contact with the air.
Food refrigeration
Nowadays, refrigeration and freezing are the two most widespread methods of food preservation.
Food refrigeration is a preservation process based on the reduction or maintenance of a controlled temperature for a given time and space, usually in cold rooms. This process is based on the extraction of energy from bodies with high thermal energy, thus reducing their energy, and consequently bacterial activity, in this case, in the preservation of foodstuffs.
When we talk about thermal energy, we refer to the temperature of a given body, since the more thermal energy, the higher the temperature of the body. Conversely, the lower the thermal energy, the lower the temperature.
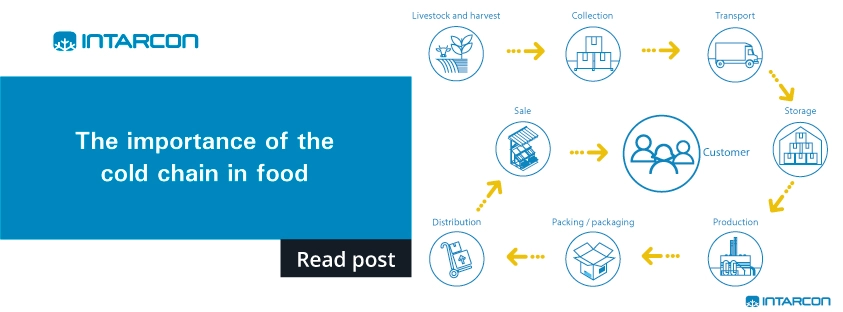
In addition, to better understand the importance of food refrigeration, it is important to know the cold chain. If we were to analyse our daily food consumption, we would see that the vast majority of them are perishable and therefore need to be refrigerated in order to be consumed in the desired time and form without altering their optimal conditions of consumption.
Food safety
There is a great deal of regulation on food safety, both at national, European and international level. As early as 1948, article 25 of the Universal Declaration of Human Rights (UDHR) states: “Everyone has the right to a standard of living adequate for the health and well-being of himself and of his family, including food, clothing, housing and medical care and necessary social services”.
How should we defrost food?
Defrosting is just as important a process as freezing if we want to obtain quality food.
In this case, the rules are just the opposite of those for a freezing process. While freezing processes should ideally be carried out in the shortest possible time, when it comes to thawing, the ideal is just the opposite, that they should be as slow as possible (within reasonable limits).
A very common practice to avoid whenever possible is to defrost food at room temperature, as there are a lot of bacteria that proliferate very easily at temperatures between 4 and 40 °C, especially in foods such as meat or fish. In addition, when thawing at room temperature, the surface of the food will inevitably thaw first, generating a layer of water on that surface which will favour the growth of these bacteria.
What is slow defrost?
Based on the above, thawing should ideally be carried out at a temperature that does not exceed this barrier, which is around 4 °C (maximum 5 °C). The disadvantage here is that defrosting will take much longer, but it will be worth it as the defrosting will be uniform. This slow defrosting helps to restore the original properties of the food, and the proliferation of bacteria will be very slow. For this reason, it is recommended at a domestic level, that defrosting of food is always carried out inside the refrigerator, where the temperature is usually around 4 °C.
What is fast defrosting?
If we do not have the time to perform slow defrosting (inside the refrigerator), there are also some quick defrosting methods that can give an acceptable result if done properly:
- Microwave: it is advisable to carry out the defrosting process in several stages, as if we do it in just one, we run the risk of cooking some parts of the food. The defrosted product should be cooked without much delay.
- Cold water jet: consists of hermetically wrapping the food and subjecting it to a jet of cold water. Since the defrosting time is relatively short, it will not be long enough to reach temperatures that put the food at risk.