Unknown and surprising R152a
INTARCON2023-01-11T17:04:42+01:00DFE, R152a or difluoroethane is an environmentally friendly medium-temperature refrigerant that replaces the refrigerant R134a. Difluoroethane is ozone friendly, has excellent thermodynamic efficiency, and has a very low global warming potential or GWP of only 124.
R152a is commonly used as a propellant in aerosols, as a foaming agent, or as a component of refrigerant blends, however, its classification as a slightly flammable refrigerant has limited its use in automotive and commercial refrigeration. However, the recent Spanish taxation of fluorinated greenhouse refrigerants (with GWP greater than 150), as well as the limitations imposed by the F-Gas regulation in the face of global warming, has led to a renewed interest in flammable refrigerants, and even highly toxic refrigerants such as ammonia.
Features of R152a
Difluoroethane or R152a is a pure fluorinated hydrocarbon with a formulation very similar to R134a. It has a vapour pressure curve equivalent to R134a, with deviations of only 2K, and has equivalent chemical characteristics, and is therefore compatible with all materials, refrigeration components, thermostatic valves, compressors and lubricating oils.
R152a also has superior thermodynamic characteristics to R134a and HFOs. The heat transfer coefficient of the refrigerant in evaporators is increased by about 20% due to the better physical properties of R152a compared to R134a. Due to the lower gas viscosity, the pressure drop in the suction lines will be reduced by 30%. The lower molecular weight of R152a gives it a high latent heat of vaporisation, a higher volumetric efficiency of the compressor, and a better COP performance of the refrigeration cycle, with a higher discharge temperature of about 10K compared to R134a.
Properties of R152a vs R134a and R1234yf (REFPROP9)
| R134a | R1234yf | R152a | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight (gr/mol) | 102 | 114 | 66 |
| Boiling temperature at atm pressure. | -26,1ºC | – 29,5ºC | – 24,0ºC |
| Latent heat of evaporation at-10ºC, kJ/kg | 199 | 163 | 307 |
| Volumetric cooling capacity, kJ/m3 | 1293 | 1186 | 1283 |
| GWP (IPCC AR4) | 1430 | 4 | 124 |
| Límite inferior de inflamabilidad %vol | – | 6% | 4% |
| Heat of combustion kJ/mol | 428 | 1220 | 1090 |
| Self-ignition temperature | – | 405ºC | 454ºC |
| ASHRAE safety class | A1 | A2L | A2 |
Thermodynamic performance
The working pressure of R152s is slightly lower (-10%) than that of R134a for the same evaporating temperature. However, its cooling capacity is equivalent (-1% compared to R134a), so R152a could be used in the same refrigeration system as a substitute for R134a.
In practice, by combining all the factors in the same refrigeration system, the energy efficiency of R152a is 20% higher than that of R134a, and even higher than that of R1234yf. Also, in the same system, the reduction of the R152a refrigerant charge is 40% by weight due to the lower molecular weight.
In the calculation of the environmental impact or TEWI factor of an installation, R152a would obtain a lower value than R1234yf, as the higher direct effect on global warming due to a higher GWP index is largely offset by the reduction of the indirect effect associated with lower electricity consumption.
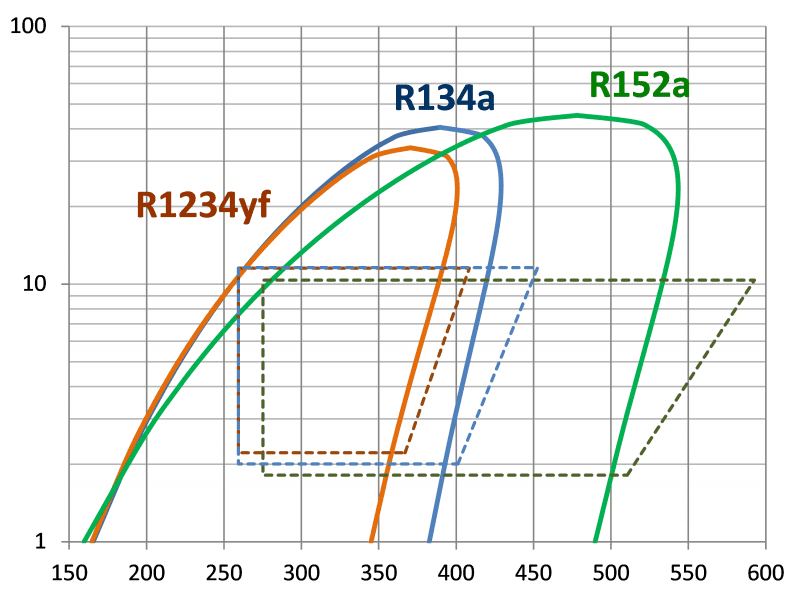
Pressure (bar) – Enthalpy (kJ/kg) diagram of different refrigerant gases
Chemical compatibility
The Air Conditioning and Refrigeration Institute of Technology report, as part of the materials and lubricant compatibility research programme prepared by the US Department of Energy in 1993, examined different HFC gases in various concentrations with various lubricants. R152a was found to be miscible at all concentrations and over the entire test temperature range of -50ºC to 90ºC.
The programme tested the compatibility of 24 materials commonly used in compressors with the various refrigerants, including R152a, and in combination with 17 lubricants, with good results.
Compatibility with different elastomers was also tested by immersing samples in the refrigerant. In general, R152a together with R134a and other HFCs showed the lowest deformations in elastomers. As with almost all refrigerants, their incompatibility with fluorinated elastomers and silicones was deduced.
Various plastics were also tested with good compatibility results with HFCs in general. ABS, however, was shown to be incompatible with R22, R32, R123, R124, R134a and R152a.
Safety requirements
R152a is classified as a medium-safe refrigerant, class A2, non-toxic but slightly flammable. While the refrigeration plant safety regulation limits the use of medium-safe refrigerants in direct expansion commercial refrigeration applications, it does allow their use without charge limit in indirect systems and in direct expansion industrial applications.
Due to the slight flammability of group 2 refrigerants, higher safety levels are required which imply specific solutions in the design of the systems together with the corresponding risk analysis. The regulation on safety in explosive atmospheres (RD 681/2003) would classify such refrigeration installations as Zone 2 risk, i.e. as working areas in which the formation of an explosive atmosphere is not likely under normal operating conditions. The classification would not, in principle, entail the application of ATEX measures, but its usefulness would only be for the purpose of establishing the areas likely to be declassified or their classification modified by the implementation of preventive measures (such as the implementation of localised extraction, ensuring sufficient natural ventilation, etc…). [4]
To mitigate the risk in cold rooms, it is recommended to install a leak detector that isolates the evaporator from the rest of the installation, thus preventing the formation of an explosive atmosphere. Indeed, the refrigerant charge remaining inside an evaporator is usually less than 20 g per m3 of cold room, well below the flammability limit of 0.137 kg/m3.
In machine rooms, it is recommended to install an automatic extraction system in case of leakage to ensure sufficient ventilation flow.
Piping in pipes that are technically watertight, e.g. around welded pipelines, does not constitute a risk area.
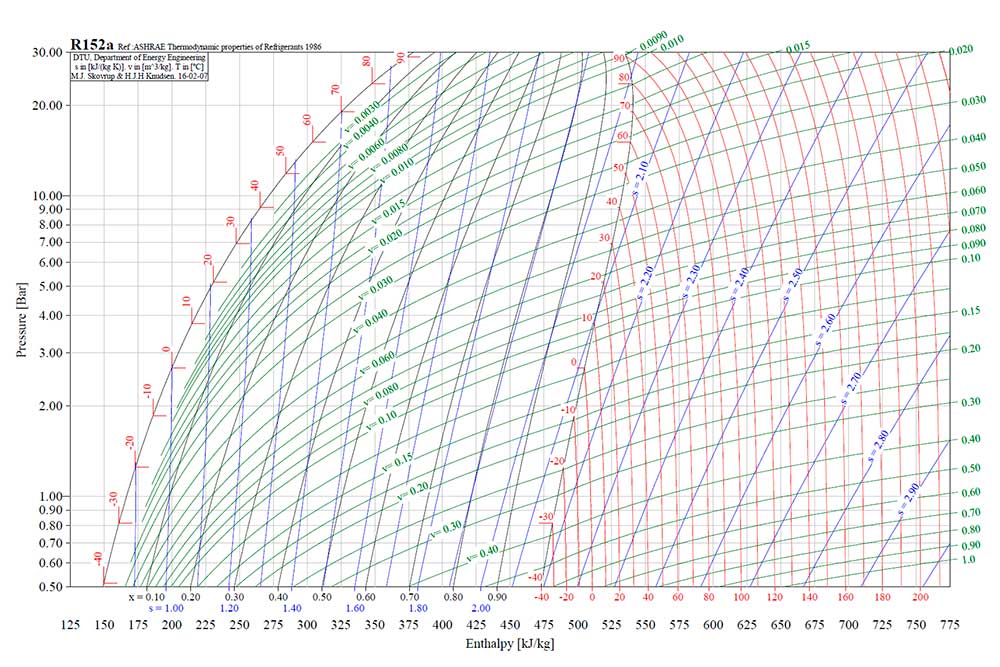
Pressure-enthalpy diagram of R152a
Literature
[6] Cabello, R (2015). Experimental comparison between R152a and R134a working in a refrigeration facility equipped with a hermetic compressor. International Journal of Refrigeration, 60, 92-105.
[8] Palm (2016-1). The opportunities and challenges of R152a, Part 1. (Möjligheter och utmaningar för R152a.) Department of Energy Technology. KTH Royal Institute of Technology. (Accedido el 30/07/2017)
[9] Palm (2016-2). The opportunities and challenges of R152a, Part 2. (Möjligheter och utmaningar för R152a.) Department of Energy Technology. KTH Royal Institute of Technology. (Accedido el 30/07/2017)
[10] UNE-EN 60079-10. Material eléctrico para atmósferas de gas explosivas. Parte 10: Clasificación de emplazamientos peligrosos.
[11] Godwin, D. (1993) Materials compatibility and lubricants research on CFC-Refrigerants substitutes. Air-conditioning and Refrigeration Technology Institute, Inc. The U.S. DEPARTMENT OF ENERGY.(Accedido el 30/07/2017).
[12] Bitzer Refrigerant Report (2014). Edition A-501-14.(Accedido el 30/07/2017)
[14] Energy performance evaluation of R1234yf, R1234ze(E), R600a, R290 and R152a as low-GWP R134a alternatives. D. Sánchez, R. Cabello, R. Llopis, I. Arauzo, J. Catalán-Gil, E. Torrella. Int. J. of Refrigeration, vol. 74, 267-280.